Now that we've reviewed the basics of setting up an Urbit React app, we can dive into the more complex logic that drives our journal app's front-end. We'll focus on the app's main component App (defined in src/app.jsx) and how it leverages functions related to ship communications using the Urbit object. For more information on UI components and other helper functions, see the resources section.
State
In the previous section, we introduced how React components use useState() to declare state variables within components. The main App component in our journal app contains a number of these statements to manage its many constituents and sub-components:
// Control/Meta State //const [subEvent, setSubEvent] = useState({});const [latestUpdate, setLatestUpdate] = useState(null);const [status, setStatus] = useState(null);const [errorCount, setErrorCount] = useState(0);const [errors, setErrors] = useState(new Map());// Journal State //const [entries, setEntries] = useState([]);const [drafts, setDrafts] = useState({});const [newDraft, setNewDraft] = useState({});const [entryToDelete, setEntryToDelete] = useState(null);// Search State //const [results, setResults] = useState([]);const [searchMeta, setSearchMeta] = useState({time: null,start: null,end: null,});
We'll see how these are used subsequently.
Initialize
After defining its state, the next thing our App component does is define a function called init(), which is one of the first functions called during its bootstrapping process:
const init = () => {getEntries().then((result) => {setSubEvent(result);setLatestUpdate(result.time);subscribe();},(err) => {addError("Connection failed");setStatus("err");});};
This function just calls getEntries() to retrieve the initial list of journal entries; then, if that succeeded, it publishes this update with setSubEvent() and setLatestUpdate() and then calls subscribe() to subscribe for new updates. If the initial entry retrieval failed, we set the connection status and save an error message in the errors map. We'll look at what we do with errors later.
Getting entries
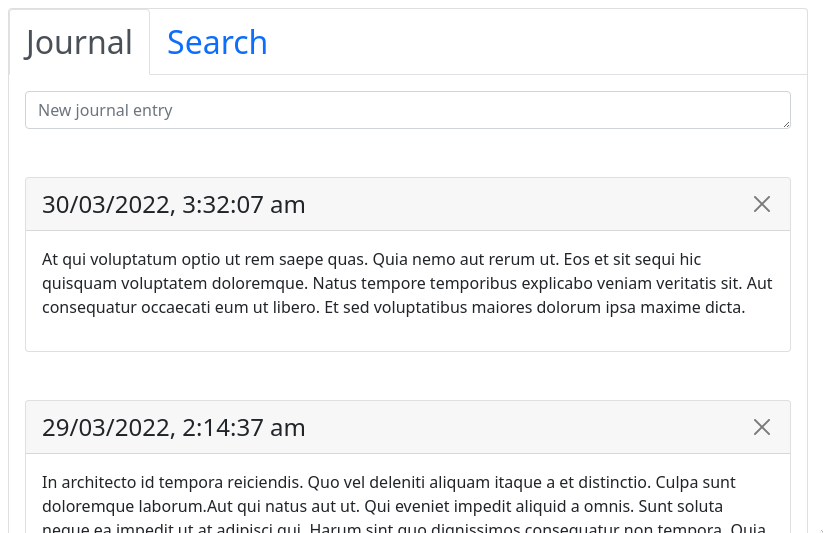
The getEntries() function scries our %journal agent for up to 10 entries before the oldest we currently have. We call this initially and then each time the user scrolls to the bottom of the list.
const getEntries = async () => {const e = entries;const before = e.length === 0 ? Date.now() : e[e.length - 1].id;const max = 10;const path = `/entries/before/${before}/${max}`;return window.urbit.scry({app: "journal",path: path,});};
The scry is done with the Urbit.scry method. This function takes two arguments in an object:
app- the agent to scry.path- the scry path. Note thecareis not included - all scries through Eyre are%xscries.
The Urbit.scry method only allows JSON results, but note that scries done via direct GET requests allow other marks too.
The Urbit.scry method returns a Promise which will contain an HTTP error message if the scry failed. We handle it with a .then expression back in the function that called it, either init() or moreEntries(). If the Promise is successfully evaluated, the results are passed to the setSubEvent() function, which appends the new entries to the existing ones via a useEffect() hook (more on this below).
Subscription
A subscription to the /updates path of our %journal agent is opened with our subscribe() function:
const subscribe = () => {try {window.urbit.subscribe({app: "journal",path: "/updates",event: setSubEvent,err: () => addError("Subscription rejected"),quit: () => addError("Kicked from subscription"),});} catch {addError("Subscription failed");}};
We use the Urbit.subscribe method for this, which takes five arguments in an object:
app- the target agent.path- the%watchpath we're subscribing to.event- a function to handle each fact the agent sends out. We call oursetSubEvent()function to set off a cascade to update the interface; this process is described below.err- a function to call if the subscription request is rejected (nacked). We just display an error in this case.quit- a function to call if we get kicked from the subscription. We also just display an error in this case.
Note that the Urbit.subscribe method returns a subscription ID number. Since we only have one subscription in our app which we never close, we don't bother to record it. If your app has multiple subscriptions to manage, you may wish to keep track of these IDs in your app's state.
Updates
The architecture for updating a React interface based on incoming facts from an Urbit subscription tends to follow a common pattern constituted of three major parts:
- A
useState()call that creates an update object field as part of the main component's state:const [subEvent, setSubEvent] = useState({}); - An
Urbit.subscribecall that passes the update object's setter function as itseventfield:window.urbit.subscribe({/* ... */, event: setSubEvent}); - A
useEffect()invocation that triggers off of the update object, which contains the logic for handling subscription updates:useEffect(() => {/* ... */}, [subEvent]);
The key piece of this architecture is the useEffect() trigger, which is called whenever an event comes in on the subscription wire (achieved by including the subscription object subEvent as a re-invocation trigger in useEffect()'s second argument). In our application, this hook is also triggered by calls to getEntries() and getUpdates(), which will be described in greater detail later.
The trigger code is a bit complex, but in broad brushstrokes it just checks the header of the incoming JSON object (i.e. one of add, edit, delete, or entries) and then updates the state appropriately. The object it's receiving is just the $update structure converted to JSON by the mark conversion functions we wrote previously.
Click to expand
useEffect(() => {const getDataIndex = (id, data) => {let low = 0;let high = data.length;while (low < high) {let mid = (low + high) >>> 1;if (data[mid].id > id) low = mid + 1;else high = mid;}return low;};const isInSearch = (id, time) => (searchMeta.time !== null &&time >= searchMeta.time &&searchMeta.start.getTime() <= id &&searchMeta.end.getTime() >= id);if (subEvent.time !== latestUpdate) {if ("entries" in subEvent) {// NOTE: `BottomScrollListener` can fire on top of `init`, which can// cause entries to be double loaded; we trim duplicates to avoid overlapconst [existing, incoming] = [entries, subEvent.entries];const oldestExistingId = existing.length === 0? Date.now(): existing[existing.length - 1].id;let newestIncomingInd = getDataIndex(oldestExistingId, incoming);newestIncomingInd += newestIncomingInd < incoming.length&& incoming[newestIncomingInd].id >= oldestExistingId;setEntries(existing.concat(incoming.slice(newestIncomingInd)));} else if ("add" in subEvent) {const { time, add } = subEvent;const eInd = getDataIndex(add.id, entries);const rInd = getDataIndex(add.id, results);const toE = entries.length === 0 || add.id > entries[entries.length - 1].id;const toR = isInSearch(add.id, time);toE && entries.splice(eInd, 0, add);toR && results.splice(rInd, 0, add);toE && setEntries([...entries]);toR && setResults([...results]);setLatestUpdate(time);} else if ("edit" in subEvent) {const { time, edit } = subEvent;const eInd = entries.findIndex((e) => e.id === edit.id);const rInd = results.findIndex((e) => e.id === edit.id);const toE = eInd !== -1;const toR = rInd !== -1 && isInSearch(edit.id, time);if (toE) entries[eInd] = edit;if (toR) results[rInd] = edit;(toE || toR) && delete drafts[edit.id];toE && setEntries([...entries]);toR && setResults([...results]);(toE || toR) && setDrafts({...drafts});setLatestUpdate(time);} else if ("del" in subEvent) {const { time, del } = subEvent;const eInd = entries.findIndex((e) => e.id === del.id);const rInd = results.findIndex((e) => e.id === del.id);const toE = eInd !== -1;const toR = isInSearch(del.id, time) && rInd !== -1;toE && entries.splice(eInd, 1);toR && results.splice(rInd, 1);(toE || toR) && delete drafts[del.id];toE && setEntries([...entries]);toR && setResults([...results]);(toE || toR) && setDrafts({...drafts});setLatestUpdate(time);}}}, [subEvent]);
Add, edit, delete
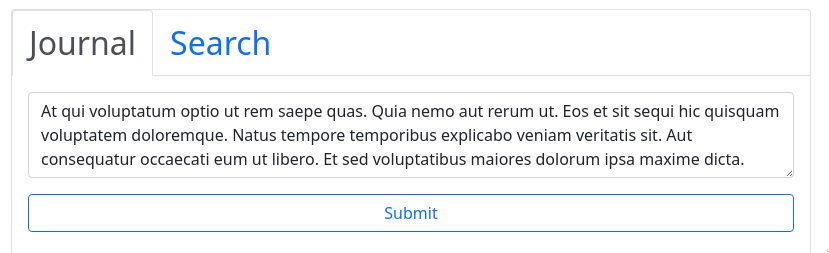
When a user writes a new journal entry and hits submit, the createEntry() function is called. It uses the Urbit.poke method to poke our %journal agent.
const createEntry = (id, txt) => {window.urbit.poke({app: "journal",mark: "journal-action",json: { add: { id: id, txt: txt } },onSuccess: () => setDraft({}),onError: () => setError("New entry rejected"),});};
The Urbit.poke method takes five arguments:
appis the agent to poke.markis the mark of the data we're sending. We specify"journal-action", so Eyre will use the/mar/journal/action.hoonmark we created to convert it to a$actionstructure with a%journal-actionmark before it's delivered to our agent.jsonis the actual data we're poking our agent with. In this case it's the JSON form of the%add$action.onSuccessis a callback that fires if we get a positive ack in response. In this case we just clear the draft.onErroris a callback that fires if we get a negative ack (nack) in response, meaning the poke failed. In this case we just set an error message to be displayed.
onSuccess and onError are optional, but it's usually desirable to handle these cases.
The deleteEntry() and editEntry() functions are similar to createEntry(), but for the %del and %edit actions rather than %add:
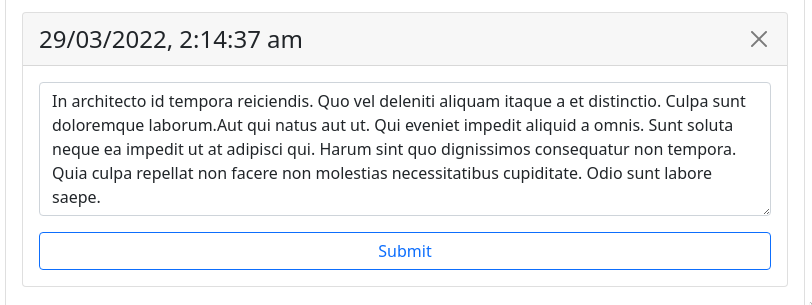
const editEntry = (id, txt) => {if (txt === null) {delete drafts[id];setDrafts({...drafts});} else {window.urbit.poke({app: "journal",mark: "journal-action",json: { edit: { id: id, txt: txt } },onError: () => setError("Edit rejected"),});}};
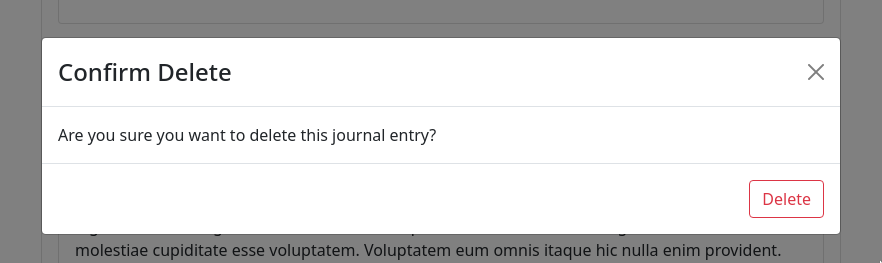
const deleteEntry = (id) => {window.urbit.poke({app: "journal",mark: "journal-action",json: { del: { id: id } },onError: () => setError("Deletion rejected"),});setDeleteId(null);};
Note that whether we're adding, editing or deleting entries, we update our state when we receive the update back on the /updates subscription, not when we poke our agent.
Search
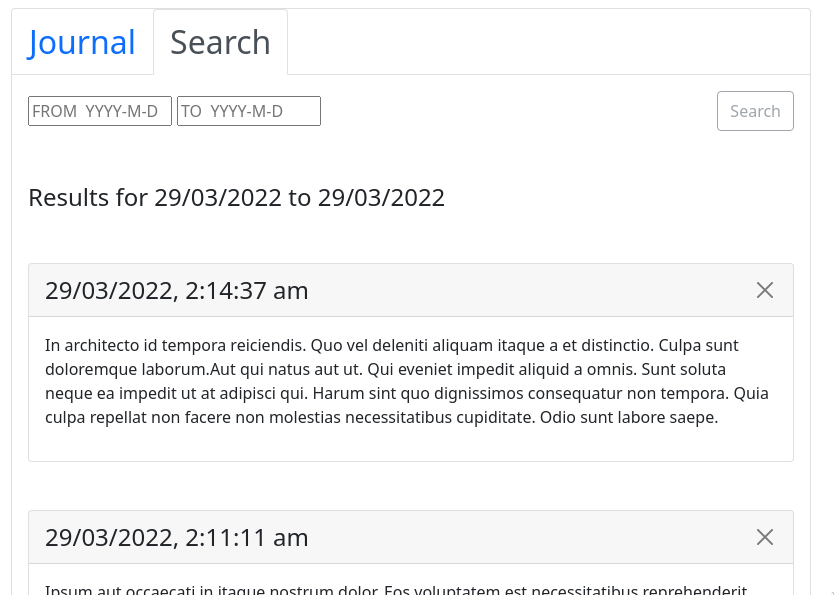
When searching for entries between two dates, the searchEntries() function is called, which uses the Urbit.scry method to scry for the results in a similar fashion to getEntries, but using the /x/entries/between/[start]/[end] endpoint.
const searchEntries = async () => {const start = Math.max(inputStart.getTime(), 0);const end = Math.max(inputEnd.getTime(), 0);window.urbit.scry({app: "journal",path: `/entries/between/${start}/${end}`,}).then((result) => {setInputStart(null);setInputEnd(null);setResults(result.entries);setSearchMeta({time: result.time,start: inputStart,end: inputEnd});},(err) => {setError("Search failed");});};
Error handling
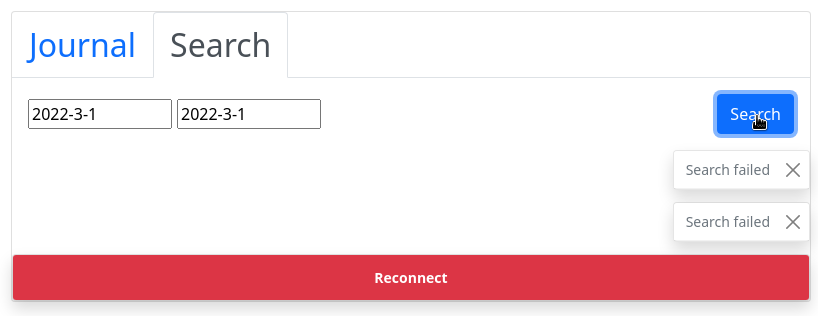
When the channel connection is interrupted, the Urbit object will begin trying to reconnect. On each attempt, it sets the connection status to "try", as we specified for the onRetry callback. When this is set, a "reconnecting" message is displayed at the bottom of the screen:

If all three reconnection attempts fail, the onError callback is fired and we replace the "reconnecting" message with a "reconnect" button:

When clicked, the following function is called:
const reconnect = () => {window.urbit.reset();if (latestUpdate === null) {init();} else {getUpdates().then((result) => {result.logs.map(setSubEvent);subscribe();},(err) => {addError("Connection failed");setStatus("err");});}};
Our reconnect() function first calls the Urbit.reset method. This closes the channel connection, wipes event counts and subscriptions, and generates a new channel ID. We could have tried reconnecting without resetting the connection, but we don't know whether the channel still exists. We could time how long the connection has been down and estimate whether it still exists, but it's easier to just start fresh in this case.
Since we've reset the channel, we don't know if we've missed any updates. Rather than having to refresh our whole state, we can use the getUpdates() function to get any missing update:
const getUpdates = async () => {const since = latestUpdate === null ? Date.now() : latestUpdate;const path = `/updates/since/${since}`;return window.urbit.scry({app: "journal",path: path,});};
This function uses the Urbit.scry method to scry the /x/updates/since/[since] path, querying the update $log for entries more recent than latestUpdate, which is always set to the last logged action we received. The getUpdates function returns a Promise to the reconnect function above which called it. The reconnect function handles it in a .then expression, where the success case passes each update retrieved to the setSubEvent() function, updating our state.
Lastly, as well as handling channel connection errors, we also handle errors such as poke nacks or failed scries by printing error messages added to the error map by the setErrorMsg() function. You could of course handle nacks, kicks, scry failures, etc differently than just printing an error; it depends on the needs of your app.
Resources
React Tutorial - A tutorial walking through the basics of writing a modern React application.
HTTP API Guide - Reference documentation for
@urbit/http-api.React app source code - The source code for the Journal app UI.
@urbit/http-apisource code - The source code for the@urbit/http-apiNPM package.